According to the latest findings SaaS industry statisticsThere are approximately 30,000 SaaS companies operating worldwide, with more than 8,550 generating over $1 million in revenue. Experts estimate that the market will grow dramatically and reach nearly $1.3 trillion by 2030.
Now is the time to start a SaaS company and get a piece of the financial pie. The question is: which SaaS product should you offer? Which business model should you choose?
Find a suitable selection below and discover the essential elements of SaaS products.
What are SaaS products?
Software as a Service (SaaS) products are cloud-based solutions that do not require downloading and installing software. They are available online for a monthly or annual fee, run on SaaS providers’ servers, and allow users to access features via web browsers and use them on the go. SaaS providers take care of maintenance, security and updates, thus relieving the burden on their customers’ IT staff.
However, you don’t have to build a SaaS product from scratch. You can purchase a white label SaaS that you can rebrand and market as your own. Think of it like leasing the software and selling it under your brand.
Crucial elements of SaaS products
All SaaS products have the following essential elements:
- accessibility – Because they are cloud-based solutions, SaaS products provide users with on-demand access, eliminating the need for downloads and installations. This means there are no setup and maintenance costs for the user, making SaaS solutions attractive to consumers.
- Scalability – Customers can scale SaaS products to fit their changing needs. They can expand capacity as their business grows or reduce it when demand is low to avoid wasting resources.
- integration – SaaS products integrate with multiple third-party apps to enable users to work seamlessly with their favorite cloud tools or on-premise systems.
- Automatic updates – SaaS providers regularly update their products to ensure they remain accessible, functional and secure. Users don’t have to worry about maintaining infrastructure or implementing the latest security measures.
These benefits make SaaS products fantastic for consumers and enable providers to continually acquire more customers and generate high revenue.
Different types of SaaS products
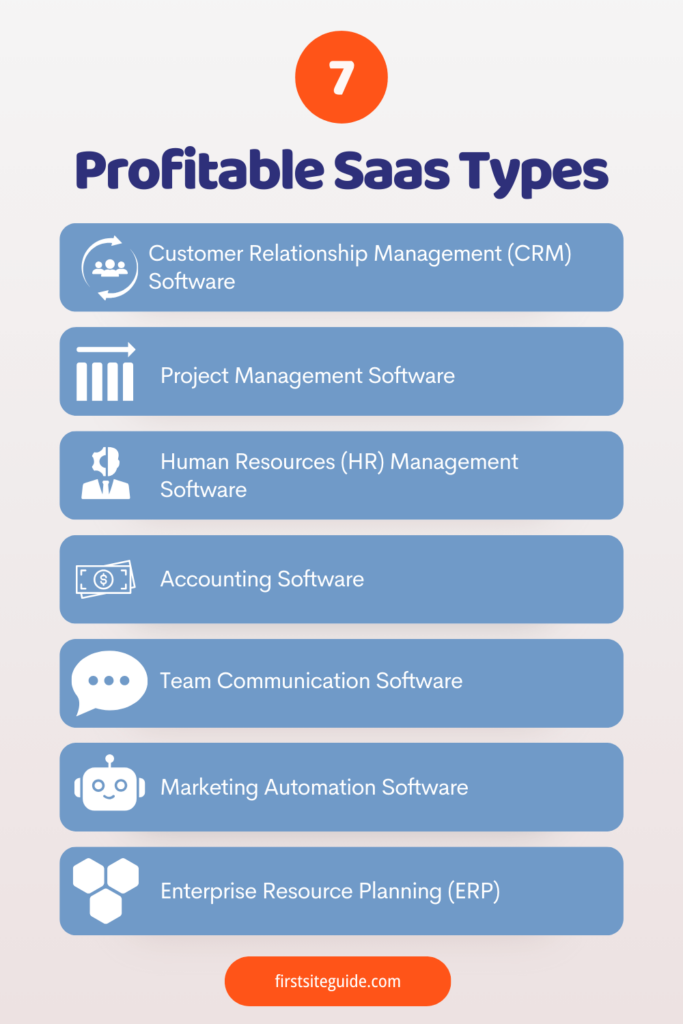
There are many types of SaaS products, the most common include the following:
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software. – a system for managing customer data (e.g. contacts, interactions and purchases), nurturing and converting leads, and building relationships. The most notable examples are HubSpot, Zendesk, Salesforce and Zoho CRM;
- Project management software – a platform for planning, scheduling, executing and monitoring tasks and projects. Confluence, Asana, Trello, ClickUp and Wrike are some examples;
- HR management software (Human Resources). – a system to optimize HR processes such as recruiting, onboarding, training, employee performance and payroll. BambooHR, Paycor, Rippling and Gusto are among the top solutions;
- Accounting software – an accounting system for recording and reporting financial transactions such as invoices, assets, inventory, income and expenses. Top-rated solutions include QuickBooks, NetSuite, FreshBooks, and Zoho Books;
- Team communication software – a real-time online collaboration platform that allows users to share files, hold virtual meetings, and increase efficiency and productivity. The most prominent players include Microsoft Teams, Slack and Zoom;
- Marketing automation software – a system for automating recurring tasks (e.g. social media and email marketing) and creating workflows. The best-known trendsetters include HubSpot Marketing Hub, Mailchimp, GoHighLevel and Salesforce Marketing Cloud;
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Software – a system designed to optimize back-office functions (e.g., human resources, accounting, process compliance, supply chain operations, and procurement). The best-known providers include Microsoft Dynamics 365, SAP and Oracle ERP Cloud.
These and other SaaS products are suitable for businesses in almost every industry, including finance, IT, retail, manufacturing, hospitality, real estate, etc.
Different SaaS business models
SaaS business models differ in their pricing structure. Here are the most common types among SaaS companies.
You don’t have to be a programmer to have a SaaS company. White label SaaS companies are a great option with low hurdles.
On a subscription basis
Subscription-based SaaS products are available for a recurring fee, typically monthly or annually. They offer a free trial or demo so users can explore all the features before committing. Pricing can be user-based, tiered, or usage-based.
Netflix is an example of a subscription-based service because users must pay to stream the video content after their free trial expires.
User based
User-based SaaS products include per-user or per-seat pricing. Businesses pay a flat rate per user and can choose between a monthly or annual plan. The more people use the product, the more sales the provider generates.
The most popular examples are Salesforce, HootSuite and Dropbox, while Slack charges for active monthly users.
Freemium
Freemium SaaS products offer free and premium plans. Free versions have limited features while their paid counterparts unlock all features. Some providers only offer one paid option, while others offer multiple as part of a tiered pricing strategy.
Many SaaS providers offer freemium products. Some examples include Asana, Trello, Zoom, FreshBooks and Mailchimp.
Graduated prices
Tiered pricing is a feature-based structure that allows businesses to choose a package that meets their needs and budget. Each higher level includes the features of the previous level and adds extras for a higher fee. Prices often include monthly rates per user.
Most SaaS companies use tiered pricing, including HubSpot, Slack, and Zendesk.
White label
White label SaaS products are unbranded solutions that companies sell to other companies. Users can rename them with their logo, colors, and other design elements and resell them for a profit. However, you still have to pay a license fee, usually a monthly or annual subscription.
Some of the best-known companies offering white label SaaS products include GoHighLevel, Sendible, Unlayer, and Ecwid.
Vertical SaaS
A vertical SaaS The business model includes SaaS products for specific industries such as retail, healthcare, education, construction, manufacturing, insurance or finance. Unlike horizontal SaaS solutions, they are not suitable for every industry or niche market. When it comes to pricing, they can include any structure their providers prefer.
Vertical SaaS providers include Riskalyze (finance), Kinnser Software (healthcare), and ServiceTitan (commercial and personal services).
Pay as you go
Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) or usage-based SaaS products allow customers to pay only for what they use, without committing to fixed monthly or annual payments. You can use all the features, but your provider only charges you a fee based on consumption.
SaaS companies that use this adaptive metered pricing model include Amazon Web Services (AWS), DigitalOcean, and WordStream. In addition to its freemium structure, Mailchimp also offers a PAYG plan.
Diploma
SaaS products are great for startups and require minimal upfront investment, especially when using a white label SaaS. They open the door to recurring revenue, high scalability and increasing customer retention rates.

