The Doj VS Google test has finally completed itself. The final document is full of interesting insights into the functioning of Google algorithms. While the final judgment of the experiment is a separate story, the published documents in Google’s ranking systems gave us an unprecedented look.
In this article I will tell what we have learned. It is wild to see how much information you gave us about Google’s ranking signals!
Part 2 of this article on what we have learned about Google’s KI systems will appear in a few days.
Tl; Dr
Google improves by learning to interact with the user. Each page is saved in the index together with signals such as clicks, queries and spam score. While Pagerank remains a signal, it is only one of many and is actually nowhere near as important as information that is stored on the website itself. AI models such as Rankembed Bert are fine through user preference and quality reviews. User data also determines how often Google crawls your pages.
Here is that Court document If you want to read it yourself.
1. Google improves through learning, interacting with the user
Google says that the key to learn to learn from learning with the user. Here are some quotes from the document:
“Learn from this user feedback Maybe the central way the web ranking has improved for 15 years. “
“Every (user) interaction gives us another example, another piece of training data: For this query, a person believed that this result would be most relevant.“
“Every time someone carries out a search, we hopefully give some useful search results, but we also receive the feedback from the crystal clear of users: This search result is better than this. “
“… There is a lot of information (about) what results are actually good or notAnd you can learn them by heart. “

Marie’s thought: Our goal should be to make content that people find helpful. The guidelines that Google gives us in theirs Helpful content documentation are not a checklist of ranking factors, but general advice, which people tend to be helpful. The actions of users teach Google which results are useful.
2. Each document in the index has a docid
Each document receives a Docid. Each Docid has a number of signals, attributes or metadata. These signals contain the popularity of the page by user clicks, their quality and authority, crawl data and a assigned spam score. While the Docid is a critical internal component for Google, it is not a metric that is publicly visible to the website owner.
Note – The Docid has been a core component of the Google Index since the start of the search. Google’s original pageran paper paper According to “on every website, an assigned ID number, which is referred to as Docid, which is assigned when a new URL is removed from a website.” Over the years, Google has expanded to what is included in the Docid.
There is a card called Docid -To -URL card.
The signals in the docid include:
- popularity Measured by user intentions, clicks and feedback systems, including Navo boost and glue.
- Quality Measures including authority
- The time of URL was first seen
- The time of The URL was last crawled
- Spam score
- Device type flag
- Every other specified signal that the (technical committee) recommends to be treated significant for the ranking of search results

3. The ranking signals contain clicks, content and queries
Google assigns a ranking score to each side and then rely on ranking signals to distinguish them.
Some of the raw signals include
- The number of clicks
- The content itself
- The terms used within a query
Marie’s thought: This does not mean that CTR is a direct ranking factor! Rather, clicks are obtained on a page that is saved and can be used in different ways. They are some of The signals that can be used in systems with which the ranking lists can determine. Further information can be found under my post Navo. While it simply has more clicks, it is a powerful, positive signal to earn clicks from users who are really satisfied with their content.
Then there are deep learning models that create other signals such as the Rankembed Bert signal.
The top ranking signals include:
- Quality
- popularity
- Signals derived from deep learning models Like rankembed bert
All of these signals can be aggregated to create even more signals. And together they are all used to generate an end result for the ranking.

4. Adhesive is a query protocol that records the activity of seekers
Google Glue is a large large table of user activity. It collects the following:
- The text of the query
- The user Language, place and device type
- What appears on the SERP (This includes the websites And SERP functions.)
- What the user clicked on Or hovered around
- How long they stayed on the snake
- Inquiry and suggestions including spelling correction and Excellent queries

Google learns from every search. The systems predict which results users find helpful, including not only websites, but also other SERP functions such as AI overviews, card lists, people also ask results and much more. Then measure how users interact with these results. The mechanical learning systems continue to learn so that they can better predict what seekers are likely to be helpful.
5. Rankembed Bert is a KI ranking model that was trained by the quality applicant and user activity
Rankembed Bert is a ranking model that is 70 days of search protocols and also the scores of the Quality value who follow one detailed guidelines for the assessment of the specialist knowledge, authority and trustworthiness of a page in order to measure the quality of Google’s organic search results. (For this reason, I created a workbook with which you can evaluate your website like a quality review.
It is a deep learning system that has a strong understanding of the natural language. The document states: “In this way, the model can identify the best documents more efficiently to access, even if a query is missing certain terms.”
Rankembed is 1/100. The data trained with which previous ranking models have been trained provides higher search results.
This system also uses information about any query in its calculations, including the Eleving terms that Google was derived from the query and the website that were recommended to the user.

Marie’s thought: In the Quality rater guidelinesIt is informed to the evaluators that “reviews are also used to improve search engines Helpful and not helpful Results With different searches, it is important to remember that an evaluator does not touch down your website directly. Instead, your collective feedback teaches the AI models, what “good” and “bad” results look, which in turn could influence how your website will be classified in the future.
Google’s deep -learning systems are far too complicated to be able to understand completely, but I think the idea is relatively easy. Similar to a voice model such as chatt, which words can be said, a ranking model predicts which pages are too rank. We know that you save the query you are looking for, the terms that are important in this query and also which actions use users. It is therefore logical to assume that these actions and the ratings of quality applicants help the model to know whether their predictions were good. If users show more signs of satisfaction and improve the ratings of the evaluators, the Algo works well. If not, the Google engineers have to work on improving things.
6. The website itself is more important than Pagerank
In my opinion, this was the most interesting in the entire document! We know this pagerank Used to be The most important signal used as an input for your quality assessment. I found it interesting that the wording that they used in this document: “Pagerank … is a single signal that refers to it Distance from a well -known good source. “”
Today Pagerank is only one of many Signals used in the ranking. Actually, It is not the most important. Google’s expert for computer science and information calls, said Dr. James Allan, “Do you understand that the most quality signal is derived from the website itself?That is quite a statement.

Marie’s thought: I think that’s incredibly important. Yes, on the left are a component of quality. But they fade compared to the signals that the website sends itself. “The most quality signal from Google comes from the website itself.” The signals in the above section are probably the most important – especially on this page and signals that come from Deep Learning models such as ranked, which continuously learn to predict which pages are probably the best result for the question of a searcher.
7. User data determines how often your pages are crawled
I didn’t know that! In the test documents it says: “Google has continuously provided User data to determine, among other things, which websites should crawlIn what order and what frequency. “

Marie’s thought: You can check your crawl statistics in the Google search console under Settings → Crawl statistics. Is Google returning regularly to crawl your website?
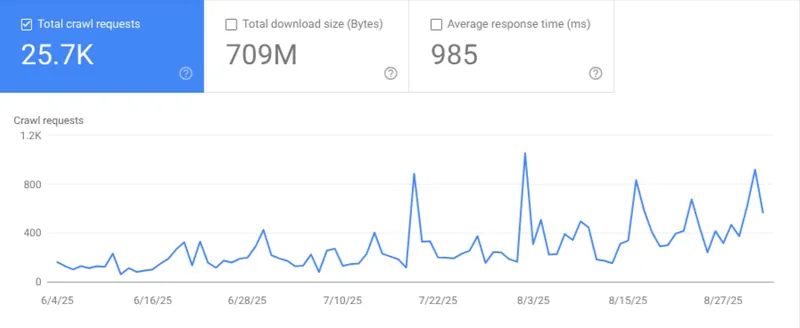
If Google creeps less frequently, this may be a sign that you have to make quality improvements or to develop an audience who is looking for your content.
I think it’s super interesting to look at the crawl purple statistics. They show you how many resources are spent on crawling your old content compared to new content that you have created. My personal thought is that when Google often crawls your website to discover new content, this is really good.

8. If they are not crabbed, this could be due to their spam points
The crawl frequency is determined by quality and popularity signals. Each side has one Spam score Which is also considered when crawling. Boy, I wish we could see the spam points of our website. If you are not sure whether you can do things that Google could see as spam, my Spam workbook can help.

9. Chroma data are used in the ranking
Oh boy, we speculated a lot about it! Here is a conversation that I had with Cindy Krum and discussed whether Signals from Chrome were used in ranking decisions. The attempt was not very detailed here, but said: “Two exhibits indicate that the popularity is based on “Chrome visit data”. and “the number of anchors”. “
Marie’s interpretation: It seems to me that the popularity that is only one of the signals used in the ranking can come from Left or from Visit and use their website. I think the latter is more important. Which is a better representation of whether people find a page that is more helpful – whether it contains links? Or whether people actively deal with the side, submit forms, buy scrolls and products? To be clear, we don’t know that Google measures these activities in Chrome, but I don’t understand why they wouldn’t do it. You would probably not be direct ranking factors. Rather, they would be all the signals that can be used to determine which pages are useful for pages.

Phew! That was a lot! There will be more. In the next few days, I will be more about what we have learned in my blog about what we have learned in the test version about Google’s AI systems, including where the training data comes – most of which is not the usual crawl – about Magit with which the text is trained in AI overviews and via Google Fast Search. Register for my newsletter if you want to be notified of the live.
If you liked that, you will love my newsletter!
Or, Accompany us in the search bar For real -time messages for SEO and KI.
Marie
More interesting reading from my blog:
How Google determines relevance and helpfulness
How Google’s helpful content system has changed the search radically
Navo and user engagement: How the hidden system from Google includes the user to form search rankings

