As I write this, the core update is introduced in June 2025. I really suspect that this update will implement a new progress that Google made in the search called Muvera.
Muvera helps Google to carry out multi-vector search as quickly as single vector search. The single vector search is quick, but sometimes misses details. The multi-vector call holds a small vector for every token on one side, which is more precise, but far too slow. Muvera closes this gap.
I think there are big impact on the search. And I’m happy about you!
Here is Google’s blog post on Muvera:
Muvera: Multi-vector call as quickly as a single vector search.
Understand muvera
Before Muvera, Google referred to something like this that was referred to as a single vector search in the top results, which were achieved by conventional methods to access information bridges. Now you can carry out a multi-vector search thanks to Muvera. The multi-vector search helps Google to find more precise matches and to record on the exact passages, sentences or even individual words that answer the question of a viewfinder.
I found it difficult to wrap my head around and spent a lot of time reading and entertaining with Gemini and Chatgpt O3 to understand what is happening here.
Single vector search for multi-vector search
During the single vector search, Google can examine a website and summarize its understanding in a list of numbers, a vector. This vector represents A point In a embedding room. The embedding room is a huge multi -dimensional map of the content on the web. Pages that discuss similar concepts will exist in this room. If a search query is embedded in this room, pages that are nearby are probably relevant.
The multi-vector search does not represent each data point as a single embedding, but as a series of embedding. In this way, the search can call up more relevant documents. The mathematical calculations that are necessary to compare a query about many embedding instead of just one is extensive! So far, the multi-vector search in a Google search system has not been used, which must return the results quickly and at minimal costs.
To make it really easy:
Single vector search Is lightning fast, but can miss details.
Multi-vector search In a document, hold a separate mini vector for every token (a character, a word or sometimes a phrase), so that it is much more precise, but far too heavy to run in real time.
Muvera enables a quick multi-vector search
Google has found out how to press the several vectors from one side into a single vector. They call it “festival -dimensional coding” (FDE). This means that you can now carry out the same type of faster search that you have carried out in this FDE during a single vector search. And surprisingly, the search queries are usually almost as accurate as if they had carried out conventional multi-vector search inquiries.
My prediction of how the core update will change the search in June 2025
Core updates are made when Google makes significant changes in its ranking systems. Lately it seems that core updates tend to choose the progress in Google’s AI functions. I think it is very likely that the Core update will introduce our first taste of Muvera in June 2025.
The core update in March 2024 happened for two weeks Google announcement of Gemini 1.5. Gemini 1.5 improved the efficiency of the mechanical learning systems from Google as well as the data you could use in calculations.
The core update in August 2024 occurred a few weeks after the announcement of Google Improvements to Gemini 1.5 lightning This made it possible to use twins much faster and cheaper.
The core update in December 2024 happened the day after Google announcement of Gemini 2.0.
The core update in March 2025 happened two weeks earlier Google publicly started Gemini 2.5.
So what about the update published today in June 2025? Maybe we will soon hear from a new version of Gemini. But I think what is more likely that the changes introduced into Google’s core ranking systems affect Muvera.
Google Open Source Die Code for Muvera. It is tempting to play with it. HoweverI change my attitude to optimize vector search. If you haven’t read it yet, I would encourage you to read this:
Could the optimization for searching for vector damage more harm than beneficial?
I think it is easy to understand how vector search works. I also think that by understanding the questions your audience has and answering it in a way that is easy to find and is analyzed is a good thing. But I think if you use tools to create content that looks like Really Good until the vector search, and users do not confirm this size. You can teach Google’s systems to downplay your relevance ratings for your website.
My advice is the same as it has been in years. Understand your audience. Make a good job to answer the questions you really have. And create resources that would consider people compared to other decisions than the most helpful of their kind.
I also think that Muvera will make Google easier to determine really original research and insight.
Did you notice how Google used in your short explanation of this current core update? They generally tell us that core updates are designed in such a way that they are better flowing out relevant and satisfactory content. But this time they added: “Of all types of websites”.
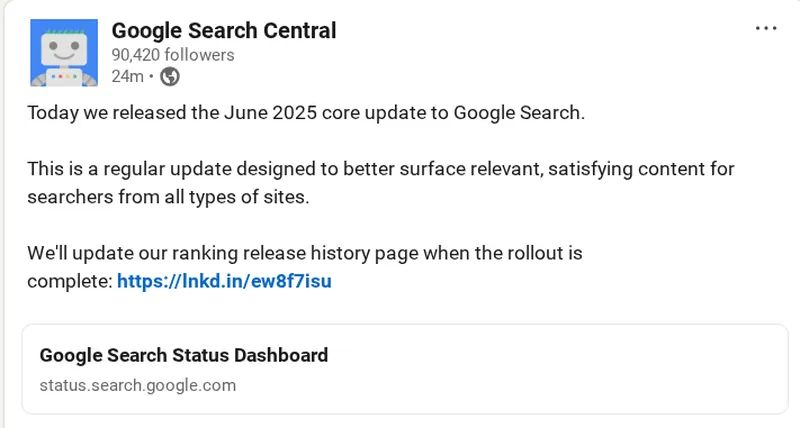
If I am right in my forecast, we will probably divide more content from smaller websites and possibly less of well -known brands.
We’ll see!
Marie
If you liked that, you will love my newsletter!
Related articles
Could the optimization for searching for vector damage more harm than beneficial?
How Google determines relevance and helpfulness
SEO in the Gemini -ära: The story of how Ai has changed Google search