Modern SEO is all about data. Ranking lists can change overnight, user behavior and search engines are increasingly using AI to supply the search results with electricity. In order to be able to answer, your decisions should be dictated by real, measurable knowledge. This article offers a practical way to transform SEO data into implementable knowledge.
The role of data in modern SEO
The search landscape is more complex than ever, so you need all the help you can get. By analyzing data, SEOs and business owners can learn and understand what works and what does not. Metrics of tools such as Google Analytics and Search console offer insights into the behavior of visitors, the use of keywords and the side performance. The use of data to make decisions takes the assumption from the SEO work.
Good data will give you a clear picture of the user. For example, the persecution of commitment period, commitment rates and click rates are shown whether the content meets the requirements of the audience. These are crucial data knowledge that reveals gaps that could hinder the performance. Data -oriented insights help you to understand what you should concentrate on and what you should focus on.
Data not only identify problems, but also opportunities. Trends in the keyword performance or a shift in traffic sources can lead to new content ideas or a new market. This is data -controlled marketing because you make decisions based on evidence instead of hunches. These findings lead to strategies that focus on real user behavior, which should lead to better results.
The goal is not to find interesting statistics – it can be found what you can do next. In the SEO and AI-controlled search, the data that includes data that leads to the action: Remove this page, move this content, change your advertisement. If your findings do not lead to decisions, they are only noise.
Carolyn Shelby – Majoro at Yoast
A Yoast example
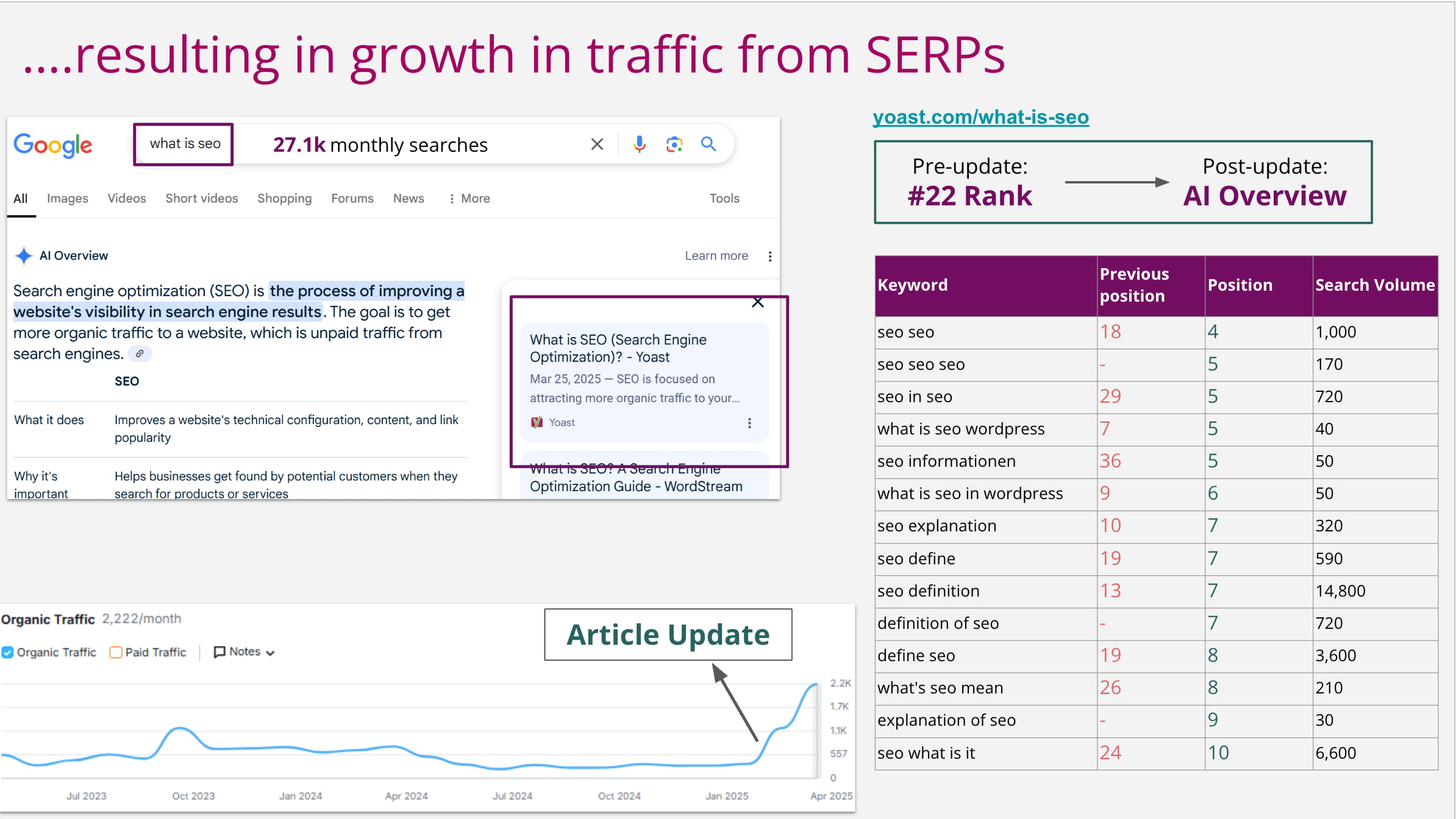
Let’s take a simple example from Yoast. We have found that one of our articles (what is SEO?) Still lost the traffic and slipped into the ranking lists in order to maintain important terms. The content had not been updated for a while, so we took a closer look. We analyzed the search results and compared our article with those of competitors. We looked at intentions, structures, relevance and freshness. It was easy to see that our article was missing in key areas depth and context.
We wrote a good order for the article and described the necessary work in detail. Then we have rewritten sections, updated examples, improved the internal link and generally read it easier. We also added new customer-specific graphics and expert quotes from one-topic from our in-house Principal SEO, Alex Moss.
After the publication, the article quickly gained visibility. It also got back to the search results that brought additional traffic. This was a clear memory for us; If data shows a decline, improving the quality of the content supported by a good analysis can still gain.
Transform data into findings
You need a process to convert raw data quickly and systematically into valuable knowledge. Finally, as soon as you ask the right SEO questions, collect, analyze, analyze and plan the right SEO questions.

Start with your goals and then ask: What does we hold back? Implementable knowledge live in the gap between the place where you are and where you try to go. This gap is different for every website and that makes a good analysis so powerful.
Carolyn Shelby – Majoro at Yoast
Step 1: What do you want to know?
First write down the SEO questions you want to answer. Would you like to improve performance, get more organic traffic or better commitment? Analyze a traffic drop? For example, an online shop owner may want to understand why certain product pages are not converted and expected so well. If you think through these things before you immerse yourself in the data, it will be easier to concentrate on the important metrics.
Step 2: Collect the relevant data
Collect the data you need with tools such as Google Analytics, Semrush, Wincher, Ahrefs or other platforms with which your data-controlled SEO strategy can be supplied with electricity. If you want to examine a product page with below-average performance, you will see page views, click rates, average engagements and engagement rates in GA4. Data like this should give you an idea of finding and tackling the problems.
Step 3: Analyze and determine trends
Immerse yourself in the data and try to recognize patterns and trends. For example, an educational center could notice that articles receive a lot of traffic on a specific topic, but a little commitment. Deeper ditch could find that the titles of the articles attract visitors, but for some reason the content does not keep you interested. Trends like this help to transform this data into knowledge to which you can react. You can also use things like segmentation to find differences between groups of people from certain regions that can be involved with their content very differently.
Step 4: Transform the results into actions
As soon as you have set the problems, it is time to decide what you want to do. For example, if you have noticed that an article has a low engagement rate due to the time required to load the page, you can fix the pictures and scripts on the page. If you find that some keywords, but no conversions receive, you may need to improve the CTA on the page. Or it can be a search intention that cannot be repaired. This is what transforms the knowledge of data into implementable knowledge.
This is a beautifully structured method to obtain the knowledge that is necessary to inform your data-controlled SEO strategy. You can use all the information you can find to improve your work in the course of your work. This not only helps you to understand the data, but also make the improvements that are necessary to achieve your SEO and business goals.
An example: respond to brand output in LLMS
For this example, think of a tech publisher called Digital Mosaic. It is a reputable source for incoming news from the tech industry. Her marketing team recently noticed something. Users interact with AI search engines and large language models (LLMS) such as Google Gemini or Chatgpt rarely mentions of the digital mosaic brand. In other words, even if they were asked about the latest technical knowledge, the AI-controlled sources and answers have often left digital mosaic in favor of other options.
After the problem was found, the team began analyzing data from various analysis platforms, brands -firing trackers and user surveys. They found that their SEO and content work was pretty good, but the content was not properly optimized to support LLMs. The data showed that its content was missing the language and brand signals that help LLMS understand the authority of the brand.
When they found this, the teams had to work on how LLMS could perceive their content:
Improvement of the brand signals
The content team added clearer brand signals to its content, and each contribution received better metadata and structured data. The aim was to clearly bind the brand to the content to help LLMs recognize the sources.
Changes to the content
Next, the team structured certain articles about brand segments such as “Digital Mosaic Exclusive Analysis” or “Tech Insights according to digital mosaic”. This makes the brand more visible to users and offers LLMS the opportunity to combine the content with the brand that comes from a trustworthy source.
Investments in partnerships and cooperation
The publisher has set up a number of cooperation with well -known technical influencers and other outlets. They made co-branded content and were mentioned in many podcasts and webinars. This contributed to improving the presence of the brand in online discussions. LLMS love to be available after what is available on third -party websites via brands and at the same time generate answers.
Rinse and repeat
The team checked the performance of the changes to determine whether the LLMs would improve the brand expectations. They used AI tools such as monitoring AI brand to monitor and simulate the LLM outputs to determine whether the work was effective. Because of their findings, they would park their work well and further improve the performance.
The results were encouraging within a few months. LLMS increasingly showed content and mentioned digital mosaic, and the footprint of the brand in LLMS improved steadily. This not only helps visibility and increased the brand’s authority in the industry, but also led to a new source of traffic from AI search interfaces.
This fictional example shows how a publisher Data knowledge can use to overcome a very specific challenge. Mixing traditional SEO solutions with new technologies helped digital mosaic to transform data into implementable knowledge. It has not only helped the visibility of the brand at the moment, but also prepared it for the AI-operated future.
Read more: How to optimize content for a Ki -llm understanding using the Yoast tools.
You need the right tools to convert data into implementable knowledge. This will be a mixture of the tools that we all know and love, and more specifically to understand the user behavior and performance of the website.
We all start with Google Analytics 4 and search console. GA4 pursues many metrics, including the user engagement, the number of events and the sources of traffic. Properly set up, there is a good overview of how users use your website. The search console shows how your website is executed in the SERPS, including keyword rankings, indexing status and crawl defects.
Tools such as Ahrefs and Semrush offer information about backlinks, rankings and search trends. These search marketing tools also have many functions for competitive analysis and keyword research. You will receive a large database with historical data so that you can recognize and interpret trends over time. This data will help you with your data -controlled marketing on all fronts.
Advanced techniques and technologies
There are so many options to dive more and more into your data to find the knowledge you need. Beyond the basics you can use:
- Segmentation: It could help divide your data into certain audience segments. For example, you can examine the visitor behavior based on demography, location or the type of device you use. By segmenting data, you can understand why certain groups behave differently. For example, if mobile users have little commitment as a desktop user, something may not be true with your mobile website.
- Trend analysis: Not only concentrate on viewing data for a specific day. It is often better to look at metrics over different periods. Take a look at the monthly or quarterly performance. This gives you an idea of the long -term effects of changes.
- Create dashboards to visualize data: Create a dashboard with data from different sources. Use tools like Looker Studio to combine Google data with SEO tools such as Semrush and Ahrefs. In this way you will receive reports that show all key data at a glance. A dashboard makes it easier to understand data and communicate with other team members or management.
- Big data: Big data is becoming increasingly important for data -controlled SEO. Huge data records can provide findings that can overlook smaller sets. They enable you to examine the user behavior, search trends and the performance of the website on a scale. With machine learning and automation, you can use big data to achieve better and faster results to inform your SEO strategy.
Iterative optimization and reporting
SEO is an ongoing process and you have to adjust the course regularly. Do not treat the performance of your website as a snapshot, but as something dynamic that develops over time. If you look at your data regularly, you can be up to date from changes in user behavior to arising search trends.
Make it a routine
Plan if you check data. This can be daily checks for urgent work or weekly to pursue short -term changes. For long -term trends, carry out deep dives monthly or quarterly. The route analysis helps you to recognize patterns that may not be so obvious at first glance.
Test and experiment
With an iterative optimization approach, test what works. For example, you can test A/B different page layouts, CTA keys or different meta titles. You can also try out different content formats to see what is more committed. You will receive these tests with the data and knowledge required to use the best of your SEO work.
Feedback loop
A real feedback loop helps to validate your improvements. Implement the changes in your content or in technical SEO work after data is converted into implementable knowledge. Update your data to determine whether you have to refine your strategy. If a new tactic works, take over it as a standard practice. But if it doesn’t work as intended, you will find out why and try a variation. Measuring the attempt and error and taking over your tactics makes you flexible and reaction quickly.
On the way to a data-controlled SEO strategy
If you use the knowledge that you get into implementable knowledge by converting data, you can significantly improve your SEO performance. Make sure that you structure the data replacement process: ask the right questions, collect the correct data, analyze the trends and create a system that converts these findings into action.
What you change on your website is not even so important. The update of metadata, improving content or diving into technical SEO aspects may be. If only what you do, the right answer to the questions you wanted.
Any findings can lead to great improvements in rankings and user engagement. Use this data-controlled marketing approach to make the right decisions that will keep your SEO strategy effective in the future.


